Wednesday, 30 August 2017
Friday, 18 August 2017
Human Endocrine System: MCQs Quiz - 1
Question 1
|
Concentration of the urine is controlled by ______
A
|
MSH
|
B
|
ADH
|
C
|
Oxytocin
|
D
|
ACTH
|
Question 2
|
Damage to thymus in children may lead to
A
|
Loss of antibody mediated immunity
|
B
|
Reduction in stem cell production
|
C
|
Reduction of hemoglobin content of blood
|
D
|
Loss of cell-mediated immunity
|
Question 3
|
ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to release a group of hormones called ______.
A
|
Mineralocorticoid
|
B
|
Glucocorticoid
|
C
|
Endorphins
|
D
|
Glucagon
|
Question 4
|
Adrenocorticotropic hormone stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce ______.
A
|
Epinephrine
|
B
|
Aldosterone
|
C
|
Cortisol
|
D
|
Testosterone
|
Question 5
|
An enlarged thyroid is the result of ______ deficiency.
A
|
Calcium
|
B
|
Iodine
|
C
|
Iron
|
D
|
Phosphorus
|
Question 6
|
Anabolic steroids are ______ versions of testosterone.
A
|
Effective
|
B
|
Synthetic
|
C
|
Natural
|
D
|
Ineffective
|
Question 7
|
The hormone known to participate in metabolism of calcium and phosphorus is
A
|
Mineralocorticoids
|
B
|
Calcitonin
|
C
|
Glucagon
|
D
|
Glucocorticoids
|
Question 8
|
Chemical signals released by an organism that influence the behavior of other individuals of the same species are called ______.
A
|
Pheromone
|
B
|
Insulin
|
C
|
Androgen
|
D
|
Steroid
|
Question 9
|
Deficiency of adrenal cortex hormones results in
A
|
Tetany
|
B
|
Acromegaly
|
C
|
Addison disease
|
D
|
Cretinism
|
Question 10
|
During growth period release of too much growth hormone can lead to
A
|
Cretinism
|
B
|
Acromegaly
|
C
|
Gigantism
|
D
|
Simmond’s disease
|
Question 11
|
Endemic goitre is a state of
A
|
Increased thyroid function
|
B
|
Normal thyroid function
|
C
|
Decreased thyroid function
|
D
|
Moderate thyroid function
|
Question 12
|
Glucagon hormone is secreted by the ______.
A
|
Thyroid gland
|
B
|
Adrenal gland
|
C
|
Pituitary gland
|
D
|
Pancreas
|
Question 13
|
Hormone responsible for the secretion of milk after parturition
A
|
ICSH
|
B
|
Prolactin
|
C
|
ACTH
|
D
|
LH
|
Question 14
|
In addition to thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3), thyroid gland produces ______
A
|
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
|
B
|
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
|
C
|
Calcitonin
|
D
|
Gonadotropic hormones
|
Question 15
|
Given below is an incomplete table about certain hormones, their source glands and one major effect of each on the body in humans. Identify the correct option for the three blanks A, B and C
GLANDS
|
SECRETION
|
EFFECT ON BODY
|
A
|
Oestrogen
|
Maintenance of secondary
sexual characters |
Alpha cells of Islets of
Langerhans |
B
|
Raises blood sugar level
|
Anterior pituitary
|
C
|
Over secretion leads to gigantism
|
A
|
B
|
C
| |
(1)
|
Placenta
|
Glucagon
|
Calcitonin
|
(2)
|
Ovary
|
Glucagon
|
Growth hormone
|
(3)
|
Placenta
|
Insulin
|
Vasopressin
|
(4)
|
Ovary
|
Insulin
|
Calcitonin
|
A
|
1
|
B
|
2
|
C
|
3
|
D
|
4
|
Digestive system and Nutrition: Quiz - 6
Question 1
|
Column I contains names of the sphincter muscles of the alimentary canal and column II contains their locations. Match them properly and choose the correct answer.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| A | Sphincter of ani internus | p | opening of hepatopancreatic duct into duodenum |
| B | Cardiac sphincter | q | between duodenum and posterior stomach |
| C | Sphincter of oddi | r | guarding the terminal part of alimentary canal |
| D | Ileocaecal sphincter | s | between esophagus and anterior stomach |
| E | Pyloric sphincter | t | Between small intestine and bowel |
A
|
A = r, B = q, C = s, D = p, E = t
|
B
|
A = q, B = t, C = p, D = s, E = r
|
C
|
A = r, B = s, C = p, D = t, E = q
|
D
|
A = s, B = r, C = p, D = q, E = t
|
Question 2
|
The diagram of large intestine of man is given below. Identify the parts labelled A, B, C, D, E and F.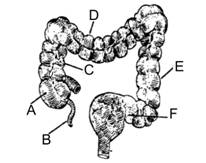

A
|
A = Caecum, B = Vermiform appendix, C = Sigmoid, D = Ascending colon, E = Transverse colon, F = Descending colon.
|
B
|
A = Sigmoid, B = Vermiform appendix, C = Ascending colon, D = Transverse colon, E = Descending colon, F = Caecum.
|
C
|
A = Sigmoid, B = Vermiform appendix, C = Descending colon, D = Transverse colon, E = Ascending colon, F = Caecum.
|
D
|
A = Caecum, B = Vermiform appendix, C = Ascending colon, D = Transverse colon, E = Descending colon, F = Sigmoid.
|
Question 3
|
Liver the largest gland is associated with several functions. Which one of the following is stated incorrectly?
A
|
Stores glucose as glycogen
|
B
|
Manufactures bile, converts the amino groups to urea
|
C
|
Makes all the cholesterol that human body needs
|
D
|
Secrete hormone called gastric
|
Question 4
|
Which one of the following statement is not correct about intestinal villi?
A
|
A multitudinous finger-like projections having many microvilli
|
B
|
Increase the internal surface area of the intestinal wall.
|
C
|
Supplied with capillaries and the lacteal vessels
|
D
|
Participate only in digestion of fats
|
Question 5
|
The following list describes four major digestive enzymes. Which one of the following is incorrect?
A
|
Salivary amylase - Salivary glands - Mouth
|
B
|
Pepsin - Gastric glands - Stomach
|
C
|
Nuclease - Small intestine - Stomach
|
D
|
Lipase - Pancreas - Small intestine
|
Question 6
|
Carrier ions like Na+ facilitate the absorption of substances like
A
|
Fructose and some amino acids
|
B
|
Amino acids and glucose
|
C
|
Glucose and fatty acids
|
D
|
Fatty acids and glycerol
|
Question 7
|
Which one of the following is the correct matching of the site of action on the given substrate, the enzyme acting upon it and the end product?
| (1) Stomach: | Fats —Lipase—► micelles |
| (2) Duodenum: | Triglycerides —Trypsin—► monoglycerides |
| (3) Small intestine: | Starch —(α)Amylase—► Disaccharide (Maltose) |
| (4) Small intestine: | Proteins —Pepsin—► Amino acids |
A
|
(1)
|
B
|
(2)
|
C
|
(3)
|
D
|
(4)
|
Question 8
|
If for some reason our goblet cells are non-functional this will adversely affect
A
|
Smooth movement of food down the intestine
|
B
|
Production of somatostatin
|
C
|
Secretion of sebum from the sebaceous glands
|
D
|
Maturation of sperms
|
Question 9
|
What will happen if the secretion of parietal cells of gastric glands is blocked with an inhibitor?
A
|
Enterokinase will not be released from the duodenal mucosa and so trypsinogen is not converted to trypsin
|
B
|
Gastric juice will be deficient in chymosin
|
C
|
Gastric juice will be deficient in pepsinogen
|
D
|
In the absence of HCl secretion, inactive pepsinogen is not converted into the active enzyme pepsin.
|
Question 10
|
A young infant may be feeding entirely on mother's milk which is white in colour but the stool which the infant passes out is quite yellowish. What is this yellow colour due to
A
|
Pancreatic juice poured into duodenum
|
B
|
Intestinal juice
|
C
|
Bile pigments passed through bile juice
|
D
|
Undigested milk protein casein
|
Question 11
|
Bile contribution to digestion is
A
|
Nucleic acid metabolism
|
B
|
Phagocytosis
|
C
|
Emulsification of dietary lipids
|
D
|
Carbohydrate digestion
|
Question 12
|
Name the hormone that stimulates the secretion of gastric juice.
A
|
Renin
|
B
|
Enterokinase
|
C
|
Enterogastrone
|
D
|
Gastrin
|
Question 13
|
Bile salts act as activator of which enzyme?
A
|
Pepsinogen
|
B
|
Trypsinogen
|
C
|
Lipase
|
D
|
Pancreatic amylase
|
Question 14
|
Aggregates of lymphoid tissue present in the distal portion of the small intestine are known as
A
|
Villi
|
B
|
Peyer’s patches
|
C
|
Rugae
|
D
|
Choroid plexus
|
Question 15
|
Which one of the followings is not part of the large intestine?
A
|
rectum
|
B
|
colon
|
C
|
cecum
|
D
|
duodenum
|
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)






